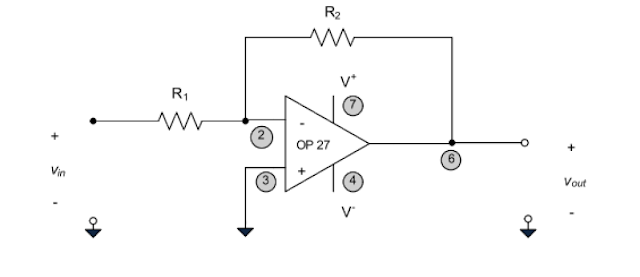
We will construct a circuit like picture below:
The polarity of the electrolytic capacitor is important, it is not symmetric like other capacitors. When we change the polarity, the behavior of capacitor can be changed as such. The longer lead will be anode(+), and the shorter lead will be cathode(-).
We also use R=100Ω, C=10μF connected in series, and power supply will be 5V. We will "disconnect" and "reconnect" the power supply to observe the behavior of capacitor when charging and uncharging.
Tau = RC= 100 * 10 * 10^(-6) = 0.001s
In order to fully charged, it will take 5T = 0.005s. In our experiment, time for capacitor to be fully charged happened quickly as well.
But when it comes to discharging, our experiment result was completely off. The reason for that would be the huge internal resistance in the circuit. Since we learned that the leakage happen when value of resistor should be around 500MΩ while we only have 100Ω.
Here is the picture of our circuit.